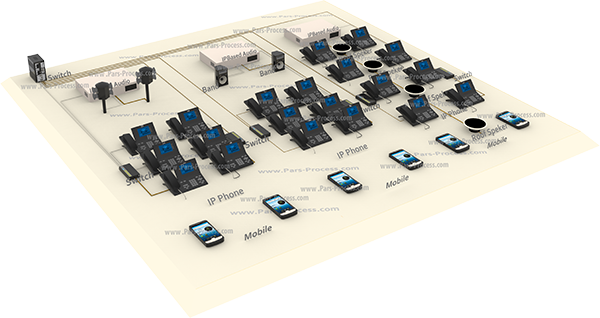
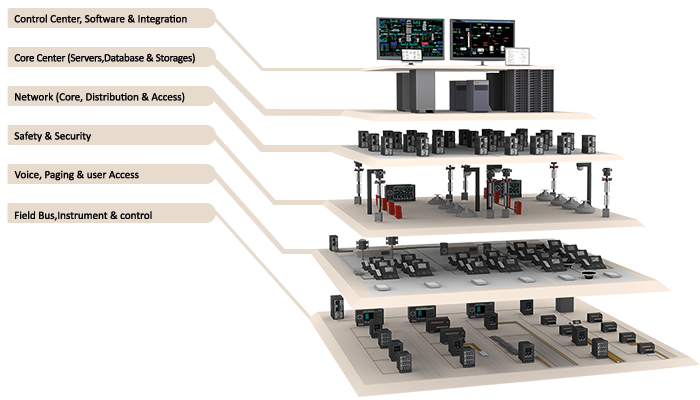
The concept BUS:
Bus transfer data between one or more devices
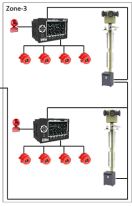
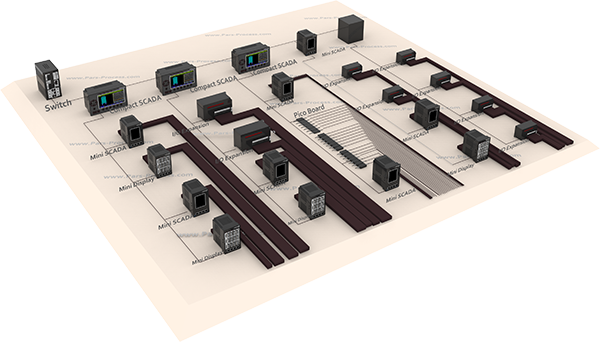
The concept Filed Bus:
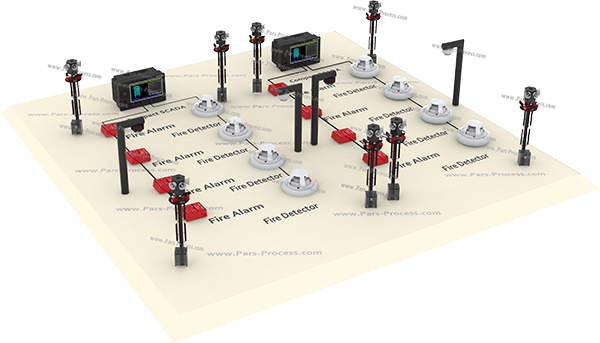
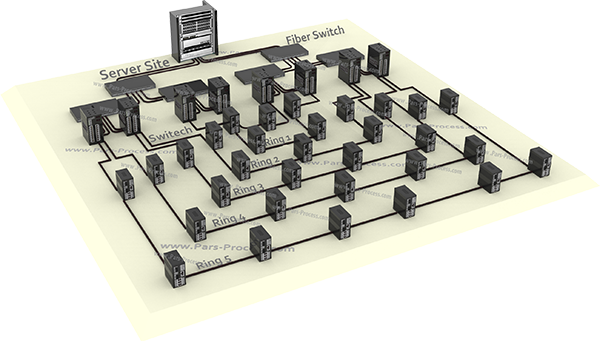
Industrial network for connecting multiple devices to control and data transfer for Real-time, which is usually distributed control system is used.
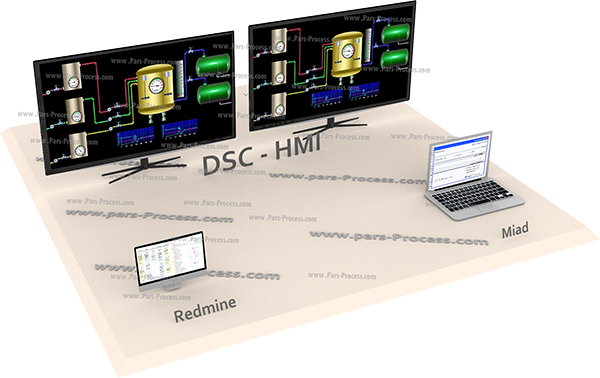
In this network as a tree, the user interface (HMI) and central control at the highest level.
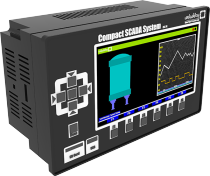
SCADA (system control and data collection):
Control and measurement system that functions as a central system, monitoring and processing the information from a site in large intervals, SCADA said.
In this system, the control room can be based on data obtained to issue the necessary instructions and data in a data storage system (database) storage.

Advantages :
1. Stability and safety
1. The use of parts and final control products and services for industrial use
2. Using redundant cabling and ready to service for passive systems
3. Real-time systems and watchdog for active service
4. Protection of devices with system overload protection, overvoltage and thermal protection
2. Cost
1. Remove the coaxial cable and exponentially decreasing the ultimate price by the price development of appropriate
2. Reduce sleep time system due to the use of redundant routes
3. The final price will be reduced by integrating various services, while maintaining redundancy
4. priced devices, with the ability to fit
5. Lower maintenance costs due to the design, implementation and maintenance by the manufacturer directly
3. Increase Productivity
1. Access to services in any place systematically
2. Implementation services to at least change after the implementation of appropriate
3. Reduce complexity and variety of maintenance by reducing the number of components in the system
4. Increased efficiency through convenient access to anywhere with a powerful platform implemented
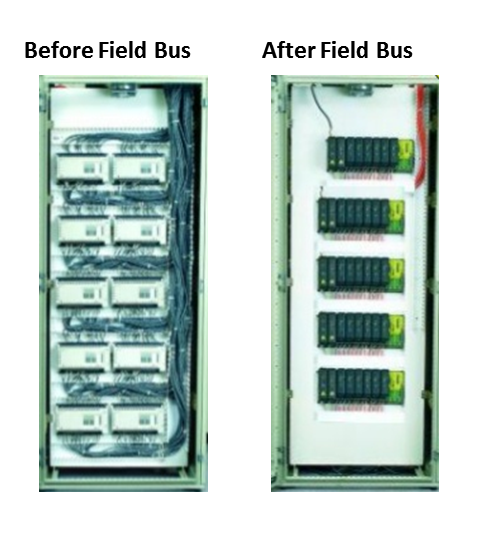
Compare variety of protocols Field Bus
| Standards | IEC 61158 | EN 50170 | Modbus-Foundation | EN 50325 | IEEE 802 and … | HART-Foundation |
| Name | Profibus | Foundation HSE | Modbus | CAN/Open | Ethernet | HART |
| Stability | Normal to high | high | high | high | high | Good |
| Cable | 2-wire | 2-wire | 2-wire | 2-wire |
Wire : 4-wire (Cat5 or Cat6) Fiber optic : 2-Fiber core |
Coax Or twisted pair |
| Maximum length | 1200 m | 1900 m | 1200 m | 40 m to 1 km |
100BaseTX=100 m 1000BaseFX=1 km to 100 km |
1000 m |
| Speed (bit rate) | 10K ~ 500K | 100 M | 1K ~ 38K | 10K ~ 1M | 100M ~ 1000M ~ 10000M | 1K * |
| Support hubs | No exist | for HSE | No exist | No exist | Yes | No exist |
|
Maximum nodes without repeaters |
32 | 8 to 16 | 2 to 32 | 64 | No limit | 15 * |
| Maximum nodes with repeaters | 126 | 8 to 16 | 2 to 250 | 127 | No limit | 15 * |
| Isolation | No (by third) | * | No (by third) | No (by third) | Yes | No |
| Support by Pars Process | By Request | Currently not plan | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Yes (Only single slave) |
Field Bus Protocols supported by Pars Process Co.
| Speed | Low | Medium | 100M star | 100M fiber star | 100M fiber ring | 1G star | 1G fiber star | 1G fiber ring | 10G fiber |
| Name |
LBus Modbus |
MBus CANopen |
100Base-TX |
HBus-s 100Base-FX |
HBus 100Base-FX |
1GBase-LX |
GBus-s 1GBase-LX |
GBus 1GBase-LX |
ZBus 10GBase-LA |
|
Speed (bit rate) |
1K to 38K | 10K to 1M | 100M | 100M | 100M | 1000M | 1000M | 1000M | 10000M |
| Distance | 1200 m | 40 m to 1 km | 100 m | 100 km | Over 500 km | 100 km | Over 500 km | Over 500 km | Over 500 km |
| Nodes count | 2 to 32 | 64 | No limit | No limit | No limit | No limit | No limit | No limit | No limit |
| Cable Price | 1x | 1x | 3x to 5x | 5x to 10x | 3x to 7x | 8x to 16x | 9x to 22x | 5x to 9x | 7x to 40x |
| Advantage |
-low price in cabling -low price in EQ. -low price in PM -Easy to enhance in node |
-low price in cabling -Medium speed -Easy to enhance in node |
-High speed -General purpose |
-Medium price in EQ. -High speed -General purpose -No noise sensitivity |
-Suitable speed -Redundant -Medium price in cabling -Easy to enhance in node -No noise sensitivity |
-Very high speed -General purpose |
-Medium price in EQ. -Very high speed -General purpose -No noise sensitivity |
-Very high speed -Redundant -Medium price in cabling -Easy to enhance in node -No noise sensitivity |
-Ultra high speed |
| Disadvantage |
-Limited number of node -Very low speed -Non isolation -No Short circuit protection |
-Limited number of node -low price in EQ. -Non isolation -No Short circuit protection -High price in PM |
-Low distance -Medium price in cabling -Noise sensitivity in long cable -No redundancy |
-High price in cabling -No redundancy -Complex implementation and PM in Large Network |
-High price in EQ. -Low speed in large number of device |
-Highprice in cabling -Noise sensitivity in long cable -No redundancy |
-High price in cabling -No redundancy -Complex implementation and PM in Large Network |
-Very high price in EQ. |
-Ultra high price in EQ. (100x to 500x) -Very high price in cabling |